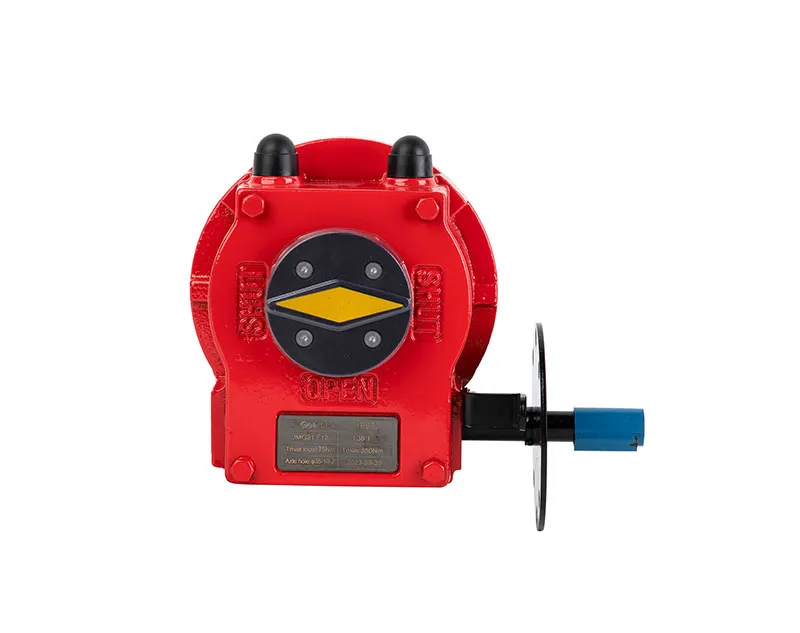
Factors Influencing The lifespan of worm gears
Worm gears are frequently employed in power transmission systems as a result of their high reduction ratios and compact design. Nevertheless, their lifespan is contingent upon a variety of factors:
Material Selection
Worm: Typically constructed from hardened steel (e.g., AISI 4140) to ensure resistance to attrition.
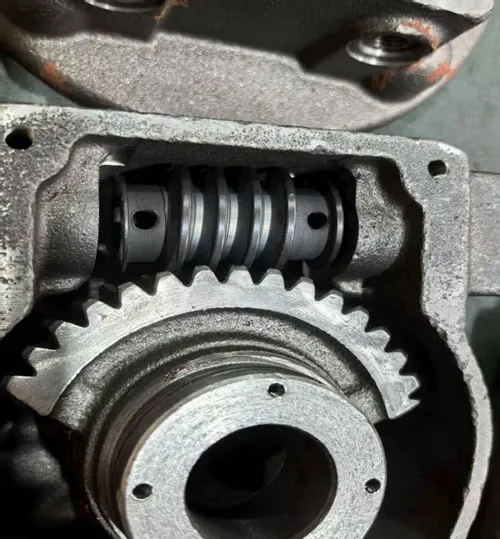

Worm Wheel: Frequently made of bronze (e.g., phosphor bronze) to minimize friction with the steel worm.
Proper lubrication mitigates erosion and heat. The use of synthetic lubricants that contain extreme pressure (EP) additives is advised.
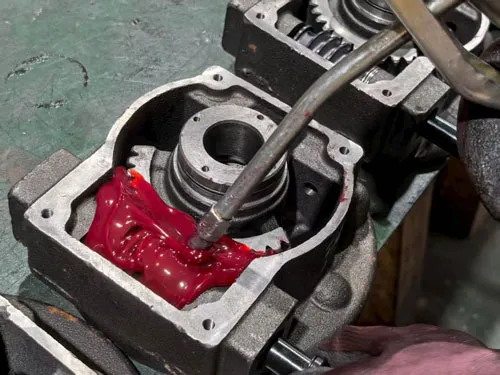
Premature failure and pitting may result from inadequate lubrication.
Torque and Load
Wear is expedited by overloading. The lifespan decreases exponentially as the burden increases, a phenomenon that is analogous to the calculation of bearing life.
Mounting and Alignment
Localized erosion and vibration are the result of misalignment, which results in uneven contact.
Operating Environment
Lubrication and materials are susceptible to degradation by dust, moisture, or corrosive compounds. In severe environments, sealed housings are indispensable.
Methods for Prolonging the Life of Worm Gear
Consistent Upkeep
Replace contaminated oil and monitor lubricant levels.
Control of Temperature
Wear is expedited by excessive temperatures. If necessary, implement forced ventilation or cooling devices.
Refrain from applying shock loads.
Micro-cracks in gear teeth are the result of sudden impacts.
Manufacturing with Precision
Smooth meshing is guaranteed by the high-quality milling of the worm.









