What Regular Maintenance Checks Can Prevent Pneumatic Valves Failures?
Troubleshooting and Precautions for Pneumatic Valves
The utilization of pneumatic valves in industrial automation control systems is widespread. Their service life can be extended and their operation can be guaranteed to be stable through appropriate use and maintenance. Below are the key precautions and common troubleshooting methods.
I. Safety Guidelines for the Operation of Pneumatic Valves
Air Supply Requirements
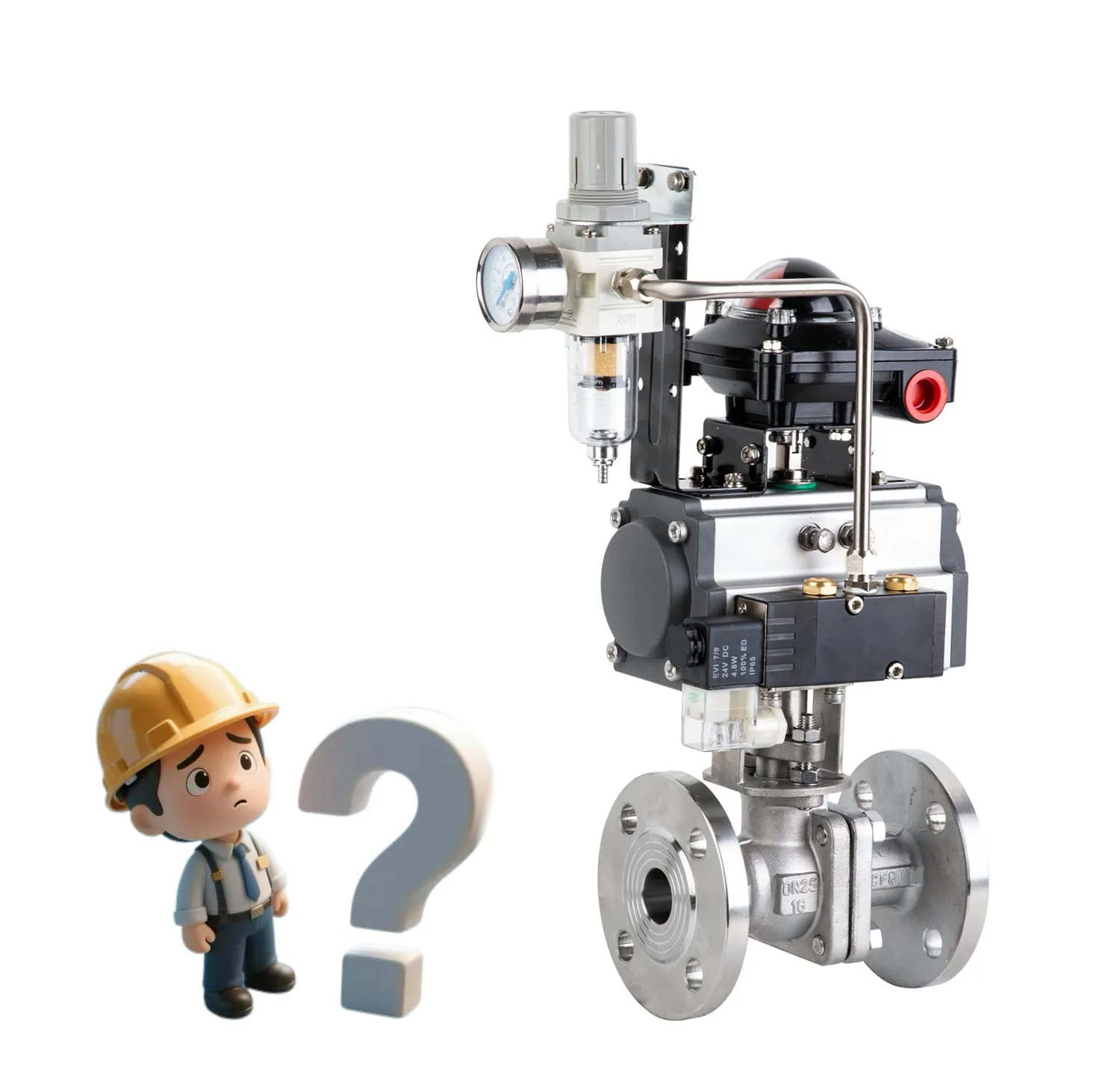
Air pressure is typically between 0.4 and 0.6 MPa (4 and 6 bar). The actuator may be damaged by excessive pressure, while the valve may not operate fully due to insufficient pressure.
Air Quality
To prevent the presence of contaminants, oil, or moisture, it is recommended to utilize clean, dry compressed air. Install an air filter and pressure regulator if necessary.
2. Installation Environment
Temperature
The majority of actuators are capable of operating within a temperature range of -20°C to 80°C. Models that are specifically designed for extreme temperatures are necessary.
Corrosion Resistance: In corrosive environments (e.g., chemical facilities, marine settings), utilize stainless steel or corrosion-resistant coated valves.
Explosion-Proof Requirements
Utilize explosion-proof pneumatic actuators in areas that are flammable or explosive.
3. Methods of Operation
Manual Operation
Certain pneumatic valves are equipped with manual overrides (handwheels or levers) that are intended for use in the event of a power or air supply failure.
Automatic Control
Operated by solenoid valves or PLCs. To prevent malfunctions, guarantee that signals are stable.
4. Maintenance
Regular Inspection: Verify that the actuator is moving smoothly and that there are no air escapes.
Lubrication: Certain actuators, such as gear-type actuators, necessitate periodic lubrication.
Seal Testing: Conduct routine inspections of valve sealing to prevent internal or external leakage.









